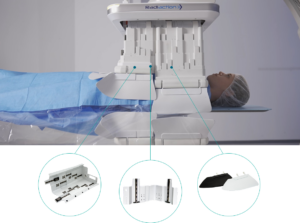
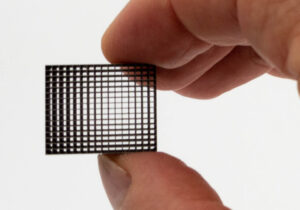
Tungsten is widely recognized for its toughness, density, and resistance to corrosion. These properties have made it a highly sought-after material across various industries, especially in the field of medicine. In recent years, tungsten has emerged as a crucial element in radiation protection, commonly used in medical appliances to shield both patients and medical personnel from harmful radiation.

Tungsten in Medicine
Tungsten, with its superior density and hardness, has been instrumental in various medical applications, primarily for radiation shielding. As a material, it provides unique advantages that are increasingly making it the preferred choice over traditional materials like lead.
Key Properties of Tungsten
Tungsten is known for its high melting point, density, and resistance to deformation under heat and other external forces. These properties make it particularly effective for shielding in environments exposed to radiation, stress, and high temperatures, such as medical imaging equipment and radiology departments.
Radiation Protection in Medical Appliances
Radiation protection is a critical aspect of many medical procedures, such as X-ray
s, CT scans, and radiotherapy. The goal is to shield patients, medical professionals, and sensitive equipment from radiation exposure. Traditionally, lead has been used in this role; how
ever, tungsten has found its way into the industry as an attractive alternative due to its high density and ability to block radiation effectively.
Why Tungsten is Essential for Radiation Shielding
The density of tungsten (up to 19.3 g/cm³ in its pure form) enables it to absorb a high degree of radiation, which is essential for protecting both patients and medical staff from ionizing radiation. Additionally, tungsten’s high atomic number enhances its ability to absorb X-rays and gamma rays, making it an ideal choice for radiation shielding.
Applications of Tungsten in Medical Equipment
Tungsten is employed in a variety of medical appliances and applications, including:
- X-ray Shields: Tungsten shields help to reduce scatter radiation.
- Radiotherapy Equipment: Tungsten collimators focus radiation on specific areas, minimizing exposure to surrounding tissues.
- MRI Shields: Tungsten is sometimes used in magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) machines due to its non-ferromagnetic properties.
- Radiation Therapy Rooms: Tungsten-based shielding in walls and barriers enhances protection.
Introduction to Poly-Tungsten
Poly-tungsten, or polymer-tungsten, is a composite material that combines tungsten with various polymers to create a material with the benefits of tungsten’s density and shielding capability, but with increased flexibility and easier handling properties.
Poly-Tungsten vs. Lead: A Comparative Analysis
While both poly-tungsten and lead provide effective radiation shielding, they differ in several key areas:
Feature – Poly-Tungsten – Lead
Density – High – High
Toxicity – Low – High
Cold Flow/Creep Resistance – High – Low
Environmental Impact – Low – High
Cost – Higher initial cost – Lower initial cost
The Advantages of Poly-Tungsten in Medical Use
Reduced Toxicity: In comparison to Lead, Poly-Tungsten is non-toxic, reducing health risks for medical staff and patients.
Environmental Safety:
Lead poses significant environmental hazards, whereas poly-tungsten is relatively eco-friendly.
Ease of Handling:
Poly-tungsten composites are more flexible than pure tungsten and require less volume than lead when seeking similar results (When comparing Poly-Tungsten 12ccm3 and Pure Lead), making them easier to incorporate into a variety of medical devices, providing the same radiation protection and weight properties for less.
Lead’s Decline in Medical Radiation Shielding
Lead has long been used in radiation protection due to its density and cost-effectiveness. However, its use is rapidly declining in the medical field due to concerns over toxicity, environmental damage, and its limitations when subjected to frequent handling or reshaping.
Toxicity of Lead and Its Health Implications
Lead is highly toxic and poses serious health risks, especially when inhaled or ingested. In medical settings, it can cause issues for both healthcare professionals and patients, leading to nervous system damage, kidney problems, and even cognitive impairments.
Environmental Impact of Lead in Medical Waste
When lead-containing medical appliances are discarded, they can contaminate soil and groundwater, posing long-term environmental hazards. Many countries are enforcing stricter regulations on the disposal of lead-based medical waste, encouraging the shift to safer alternatives like tungsten.
Tungsten as a Safer, More Sustainable Alternative
Tungsten is non-toxic and highly durable, reducing both the health risks and environmental impact associated with lead. It is increasingly used in medical devices that need to be safe for both the user and the environment, from surgical instruments to radiation shielding.
Future Prospects: Tungsten in Advanced Medical Technologies
The versatility of tungsten continues to make it valuable in emerging medical technologies, such as advanced imaging techniques and precision radiotherapy. As medical equipment evolves, tungsten is likely to play a larger role in new applications that require both strength and high radiation absorption.
Challenges and Limitations of Tungsten
While tungsten offers numerous advantages, it does have some limitations. These include:
Cost:
The cost of Pure Tungsten and Poly-Tungsten raw materials is higher than lead, which can be a barrier for some facilities and requires that the client chooses the applications mindfully, considering costs and balancing other economical parameters (NRE, Production, Material Waste, etc.)
Machinability:
Tungsten (Pure Tungsten/Tungsten Heavy Alloys) is harder to shape than lead, requiring specialized tools and techniques for processing.
The Future of Tungsten in Radiation Protection
As the medical industry increasingly prioritizes patients and environmental safety, tungsten (Pure Tungsten, Tungsten Heavy Alloys, Poly-Tungsten) is positioned to replace lead in many applications. Its high density, low toxicity, and environmental sustainability make it a safer, more practical choice for radiation shielding in medical appliances. As technology progresses, the role of tungsten is set to expand, revolutionizing radiation protection and bringing significant benefits to both healthcare professionals and patients.